Derived from the Greek plastikos, meaning “to mold or give form”, plastic surgery is a surgical procedure specializing in the restoration and improvement of function previously hindered by illness, trauma or congenital defects; and also to improve the aesthetic appearance of individuals.
Plastic surgeons generally imply that plastic surgery can be performed on any part of the body save for the central nervous system. Plastic surgery is also an umbrella term – it’s a surgical specialization that can actually be broken down into two sub-specializations: cosmetic surgery and reconstructive surgery.
Cosmetic or aesthetic surgery is dedicated to the modification and enhancement of an individual’s physical appearance, usually without the issue of a prevailing medical condition. Some of the goals of cosmetic surgery include improving the aesthetic appeal, proportion and symmetry of the patient; as well as the position, texture, structure and color of the body. Since the modified area functions normally, cosmetic surgery is defined as “elective surgery” – this means that the procedure is planned in advanced.
There are four general types of cosmetic procedures and these include:
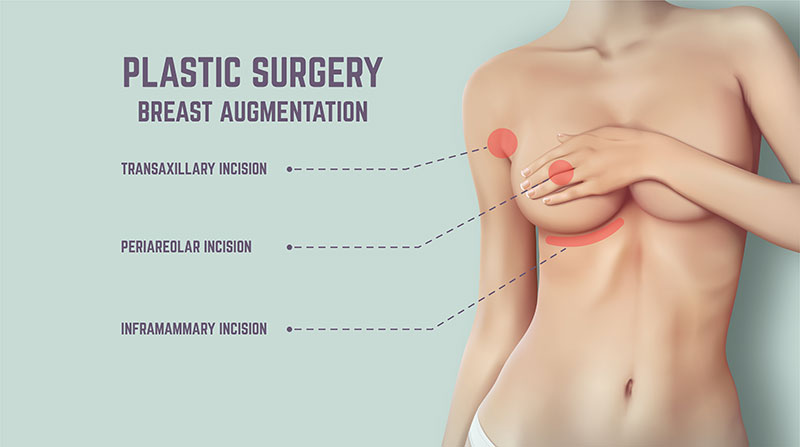
- Breast enhancement, which involves augmentation, reduction and lifts.
- Facial contouring, which involves rhinoplasty, otoplasty, and cheek or chin enhancements
- Facial rejuvenation, which involves facelifts, neck lifts, brow lifts, eyelid lifts
- Skin rejuvenation, which involves laser resurfacing, filler treatments and Botox to combat wrinkles
One benefit of cosmetic surgery is that is helps boost an individual’s self-esteem. It’s of no surprise that when an individual is satisfied with how they look, they feel more confident and self-assured, which in turn increases their self-esteem, which improves their quality of life.

A second benefit of cosmetic surgery is that it helps reduce and hide the obvious signs of aging. As a society conditioned to look as youthful as possible for as long as possible, cosmetic surgery can help “turn back the clock” on a patient’s body by addressing wrinkles, flaccid or sagging skin and aging spots through different cosmetic procedures.
A third benefit of cosmetic surgery is that it has now become more accessible and affordable for people thanks in part to advancements in medicine. The improvements in techniques, equipment and procedures coupled with an ever expanding array of practitioners in this field have allowed individuals from all echelons of society to address their aesthetic issues surgically on low or high incomes.
On the flip side, a drawback of cosmetic surgery is that some procedures can be quite costly, especially if the procedure requires multiple surgeries. While cosmetic surgery has become more affordable, it is dependent on what work the patient wants done and should multiple surgeries be necessary, the total cost can quickly add up.
Another drawback of cosmetic surgery is that for some individuals, it can become an addiction. Addiction to cosmetic surgery may be born from a psychological disorder known as Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD) – it’s a condition that causes the afflicted to become obsessed with a facial defect they may have. People with BDD and an addiction to cosmetic surgery can quickly rack up debts trying to achieve perfection under the knife and this can in turn disrupt their professional and personally lives.
The second sub-specialization of plastic surgery is reconstructive surgery. Reconstructive surgery specializes in restoring and improving the function and normal appearance of an individual caused by congenital defects, trauma or medical conditions. In most cases, reconstructive surgery is defined as a medical necessity and therefore normally covered by the patient’s health insurance.
There are generally six common types of reconstructive surgery and these include:
- Skin cancer removal, which is a surgical procedure designed to treat skin cancer, remove abnormal skin growths and restore the skin’s normal appearance.
- Cleft lip and palate surgery, which is a surgical procedure normally performed on infants and young child born with the defect.
- Scar revision, which is a surgical procedure designed to improve upon the appearance of scars brought on by past surgeries or trauma.
- Burn reconstruction, which is a surgical procedure for burn victims. The aim of this procedure is to restore function and to improve the appearance of the patient’s skin.
- Breast reconstruction, which is a surgical procedure that involves using different techniques to restore the shape, appearance and size of a patient’s breasts following a mastectomy or lumpectomy.
- Tissue transfers or tissue flap transplants, which is a surgical procedure designed to restore parts of a patient’s body to their original look and feel. The process involves using tissue, skin, fat, muscle, nerve or bone either from the patient’s own body or a deceased donor.
A benefit of reconstructive surgery is that is helps improve and “normalize” the patient’s appearance, which in turn offers them a better quality of life – professionally and personally. Having access to a better quality of life includes improving the patient’s self-esteem and emotional wellbeing, which can only boost their potential and successes professionally and personally.
A second benefit of reconstructive surgery is that it can be life-saving for the patient. Unlike cosmetic surgery, reconstructive surgery is sometimes known as urgent or emergency surgery, which indicates that the patient needs the surgery in order to survive. Reconstructive surgery is dedicated to ensuring that patients burdened with issues brought on by illness, trauma or congenital defects have the opinion to correct the problem and go on to live a better life.

A disadvantage of reconstructive surgery is that like with any kind of surgery, there are risks involved and the risks may be higher or lower depending on what medical issue the patient has. Age can also be a factor when it comes to reconstructive surgical procedures – the risks of surgery performed on a newborn or small child for example, may be greater than surgery performed on a healthy adult.
Another disadvantage of reconstructive surgery is cost – while many reconstructive surgeries can be covered by a patient’s health insurance in various countries; those without health insurance or whose health insurance doesn’t cover the procedure may find themselves unable to pay their resulting hospital bills. In conclusion, whether you decide to opt for surgery to achieve an aesthetic goal or correct a defect as a result of illness or trauma, you should consider all the advantages and disadvantages that come with the surgical procedure you intend upon or need. You should also try to gather as much information about the procedure as you can and ensure that the hospital you have your surgery in is well equipped and established; and the surgeon you select is an expert in their chosen field.